Bitcoin address
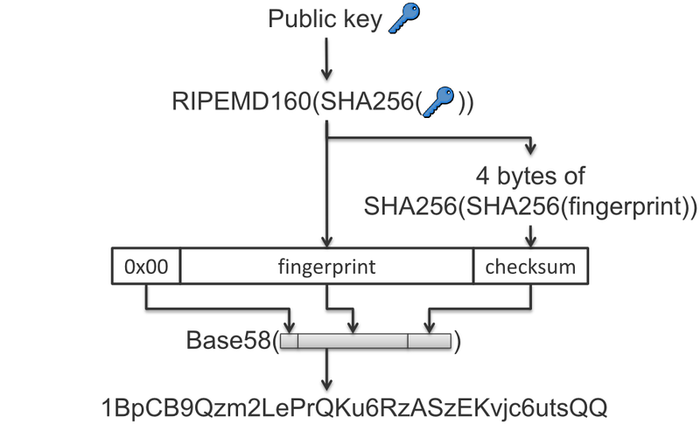
Bitcoin address is an identifier (account number), starting with 1 or 3 and containing 27-34 alphanumeric Latin characters (except 0, O, I). Bitcoin addresses can be also represented as a QR-code. The addresses are anonymous and do not contain information about the owner. A bitcoin address can be obtained for free, using, for example, Bitcoin software. Bitcoin address example:
14qViLJfdGaP4EeHnDyJbEGQysnCpwk3gd
Addresses can be generated at no cost by any user of Bitcoin. For example, using Bitcoin Core, one can click “New Address” and be assigned an address. It is also possible to get a Bitcoin address using an account at an exchange or online wallet service.
There are currently two bitcoin address format in common use:
Common Pay-to-Pubkey Hash (P2PKH) which begin with the number 1. Newer Pay-to-Script Hash (P2SH) type starting with the number 3, eg: 35bSzXvRKLpHsHMrzb82f617cV4Srnt7hS.
Contents
What’s in a Bitcoin address
Most Bitcoin addresses are 34 characters. They consist of random digits and uppercase and lowercase letters, with the exception that the uppercase letter “O”, uppercase letter “I”, lowercase letter “l”, and the number “0” are never used to prevent visual ambiguity.
Some Bitcoin addresses can be shorter than 34 characters (as few as 26) and still be valid. A significant percentage of Bitcoin addresses are only 33 characters, and some bitcoin address length may be even shorter.
Every Bitcoin address stands for a number. These shorter addresses are valid simply because they stand for numbers that happen to start with zeroes, and when the zeroes are omitted, the encoded address gets shorter.
Several of the characters inside a Bitcoin address are used as a checksum so that typographical errors can be automatically found and rejected. The checksum also allows Bitcoin software to confirm that a 33-character (or shorter) address is in fact valid and isn’t simply an address with a missing character.
Purpose and opportunities
Transfer/receive transactions of Bitcoins (Cryptocurrency, BTC) can be performed via address like the work with e-mail messages. One person can create an unlimited number of addresses, increasing the anonymity level of the payments. When performing the next transaction with BTC a new address is often created (the funds are credited/debited within 1-2 hours). At the same time the private key pair is generated, providing access to the identifier and the ability to perform transactions with currency. They are stored in the wallet.dat file on the user’s computer.
Input conditions
In order to avoid errors when manually inputting the address, it is recommended to use the clipboard. Symbols register is considered when you manually input the address. In case of incorrect input Bitcoins are sent to the wrong address or the transaction is rejected. Last one is done automatically if the identifier contains symbols that are used as a checksum (for verification).
The probability that a mistyped address is accepted as being valid is, approximately 1 in 4.29 billion.
How to create Bitcoin address?
The address is created by generating of random numbers and performing specific mathematical operations. It does not require Internet connection and registration at Bitcoin, where it begins to be monitored. Thousands of addresses (including personalized) and keys thereto can be generated within 1 minute, for example, when using Vanitygen utility.
Creating bitcoin address can be done without an Internet connection and does not require any contact or registration with the Bitcoin network. It is possible to create large batches of addresses offline using freely available software tools. Generating batches of addresses is useful in several scenarios, such as e-commerce websites where a unique pre-generated address is dispensed to each customer who chooses a “pay with Bitcoin” option. Newer “HD wallets” can generate a “seed” token which can be used to allow untrusted systems (such as webservers) to generate an unlimited number of addresses without the ability to spend the bitcoins received.
Transactions
- Main article: Bitcoin transaction
Record of the BTC transfer from one address to another generates a transaction. It contains the hash of the previous transaction signed by the sender and Bitcoins recipients address. All information is sent to the Bitcoin network and after signatures verification transaction is accepted for processing.
Most Bitcoin wallets have a function to “sign” a message, proving the entity receiving funds with an address has agreed to the message. This can be used to, for example, finalise a contract in a cryptographically provable way prior to making payment for it.
Some services will also piggy-back on this capability by dedicating a specific address for authentication only, in which case the address should never be used for actual Bitcoin transactions. When you login to or use their service, you will provide a signature proving you are the same person with the pre-negotiated address.
It is important to note that these signatures only prove one receives with an address. Since Bitcoin transactions do not have a “from” address, you cannot prove you are the sender of funds.
Current standards for message signatures are only compatible with “version zero” bitcoin addresses (that begin with the number 1).
Bitcoin Address Validation
If you would like to validate a Bitcoin address in an application, it is advisable to use a method rather than to just check for string length, allowed characters, or that the address starts with a 1 or 3. Validation may also be done using open source code available in various languages or with an online validating tool.
Loss of Bitcoins
Loss of Bitcoins is possible in the following situations:
- if the wallet is lost because of the hard drive failure,
- when generating a new address, getting BTC on it and restoring the wallet from an earlier backup, where address is not yet created,
- when sending Bitcoins to address that doesn’t have owner.
Multi-signature Bitcoin address
Addresses can be created that require a combination of multiple private keys. Since these take advantage of newer features, they begin with the newer prefix of 3 instead of the older 1. These can be thought of as the equivalent of writing a check to two parties – “pay to the order of somebody AND somebody else” – where both parties must endorse the check in order to receive the funds.
The actual requirement (number of private keys needed, their corresponding public keys, etc.) that must be satisfied to spend the funds is decided in advance by the person generating this type of address, and once an address is created, the requirement cannot be changed without generating a new address.
Address balances
Addresses are not wallets nor accounts, and do not carry balances. They only receive funds, and you do not send “from” an address at any time. Various confusing services and software display bitcoins received with an address, minus bitcoins sent in random unrelated transactions as an «address balance», but this number is not meaningful: it does not imply the recipient of the bitcoins sent to the address has spent them, nor that they still have the bitcoins received.
An example of bitcoin loss resulting from this misunderstanding is when people believed their address contained 3 BTC. They spent 0.5 Bitcoins and believed the address now contained 2.5 BTC when actually it contained zero. The remaining 2.5 Bitcoins was transferred to a change address which was not backed up and therefore lost. This has happened on a few occasions to users of Paper wallets.
«From» addresses
Bitcoin transactions do not have any kind of origin-, source- or «from» address.